Learnings from Europe on Futures Power Trading Strategies
As Japan moves towards a carbon-neutral future, the country’s power sector is undergoing significant transformation. One area of growing interest is power trading, particularly in the futures market. By examining how Europe has developed its power trading strategies and markets, Japan can learn valuable lessons to accelerate its own energy transition, improve energy efficiency, and ensure price stability.
Forfatter
Fumi Kumagai
Publisert
2. des. 2024

What is futures power trading?
In simple terms, futures power trading involves buying or selling electricity at a predetermined price for future delivery on the weekly to yearly basis. This type of trading provides a way for utilities, suppliers, and large consumers to hedge against spot price fluctuations in the electricity market. It also encourages stability by allowing market participants to manage risk associated with volatile energy prices, making it a powerful tool for risk management.
Why look to Europe?
European markets are advanced in their adoption of renewable energy, with many nations setting aggressive targets to reduce their carbon footprint. European power markets, especially interconnected systems like Nord Pool in the Nordics and EPEX SPOT in Central Europe, have established themselves as pioneers in power trading, especially for futures contracts. Japan can look to Europe’s experience to implement effective strategies and policies for power trading.
Enhanced market competition
The European Union (EU) has a liberalised electricity market, which allows multiple players to compete in power generation, distribution, and retail. This has led to more competitive pricing and greater innovation in trading strategies. Similarly, Japan has taken steps to liberalise its electricity market, but there’s more to be done. Especially in enhancing competition, Japan can attract more players to the market, leading to better price stability and diverse sources of energy. When compared to the speed of the development in the European market over the past 20 years, the growth potential of the Japan market is remarkable as visualised in the chart below.
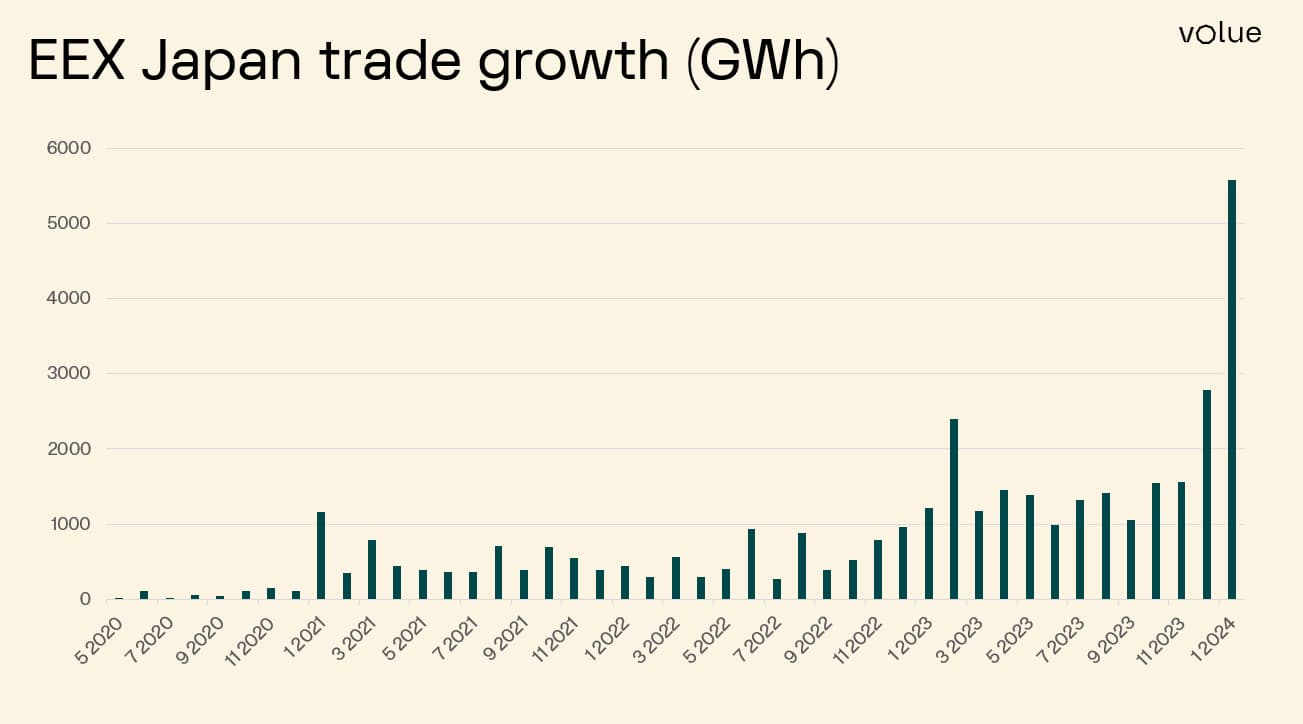
Source: EEX Japan
Growth of renewable energy
European countries have made significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure and have developed strong grid connections across borders. This has enabled efficient integration of renewable energy sources and has led to innovative trading practices.
The diversification of trading participants in Japan has been progressing, driven by the growth of renewable energy since the introduction of the FIT scheme and now the FIP scheme. However, Japan's island geography limits the kind of interconnected grid infrastructure seen in Europe. However, by investing in robust grid technologies and storage solutions, Japan can improve its power trading potential and enhance resilience against natural disasters.
Leveraging data and technology for efficient trading
In Europe, advanced technology, including AI and machine learning, helps manage power trading efficiently. These technologies analyse historical data, weather forecasts, and market trends to make accurate predictions, facilitating automated trading decisions.
Japan can adopt similar technologies to better manage power demand and optimise the distribution of energy. Additionally, having real-time data on supply, demand, and price trends could improve Japan’s trading accuracy and help balance supply with demand fluctuations.
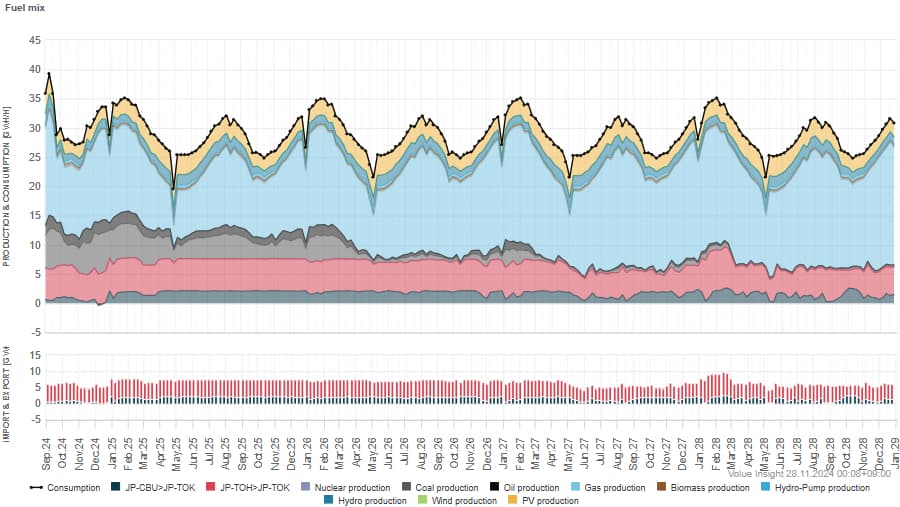
Source: Insight by Volue "Japan Forward"
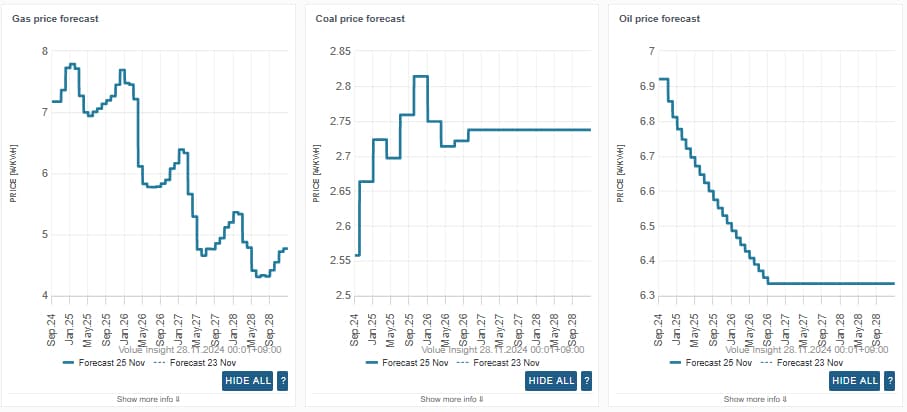
Source: Insight by Volue "Japan Forward"
Developing long-term strategies through futures contracts
European markets make extensive use of futures contracts to hedge against price volatility, making it easier for both suppliers and consumers to manage costs and revenues in the long term.
In Japan, increasing confidence in the market is further attracting domestic and international participants. As the accumulation and sharing of knowledge on the use of electricity futures as a hedge is progressing, a virtuous cycle has been created in which an increase in volume leads to an increase in participants as futures contracts offer Japanese utilities a way to secure energy prices well into the future. This could be especially useful in stabilising prices for renewable energy, which can be more variable than traditional energy sources.
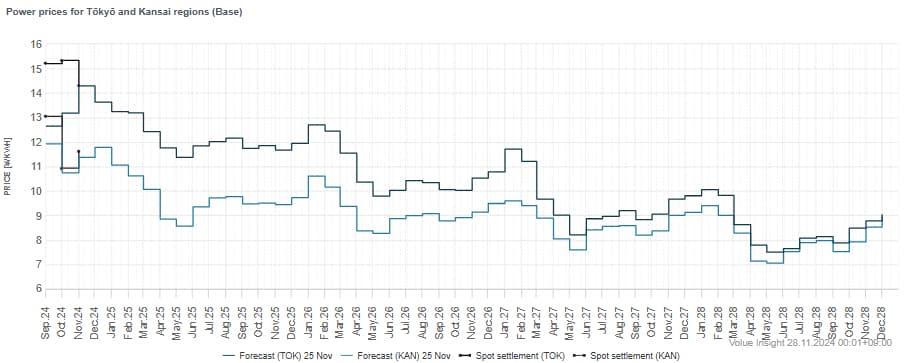
Source: Insight by Volue "Japan Forward"
Building a resilient future for Japan’s power market
Japan stands to benefit greatly by learning from Europe’s approach to futures power trading. As renewable energy sources continue to grow, futures contracts offer a way for Japanese companies to stabilise energy prices and reduce reliance on imported fuels. With strategic planning, regulatory support, and investment in infrastructure, Japan can build a resilient and efficient power market that aligns with its sustainability goals.
